Automate ERC20 token balance maintenance using a Forta bot and Actions
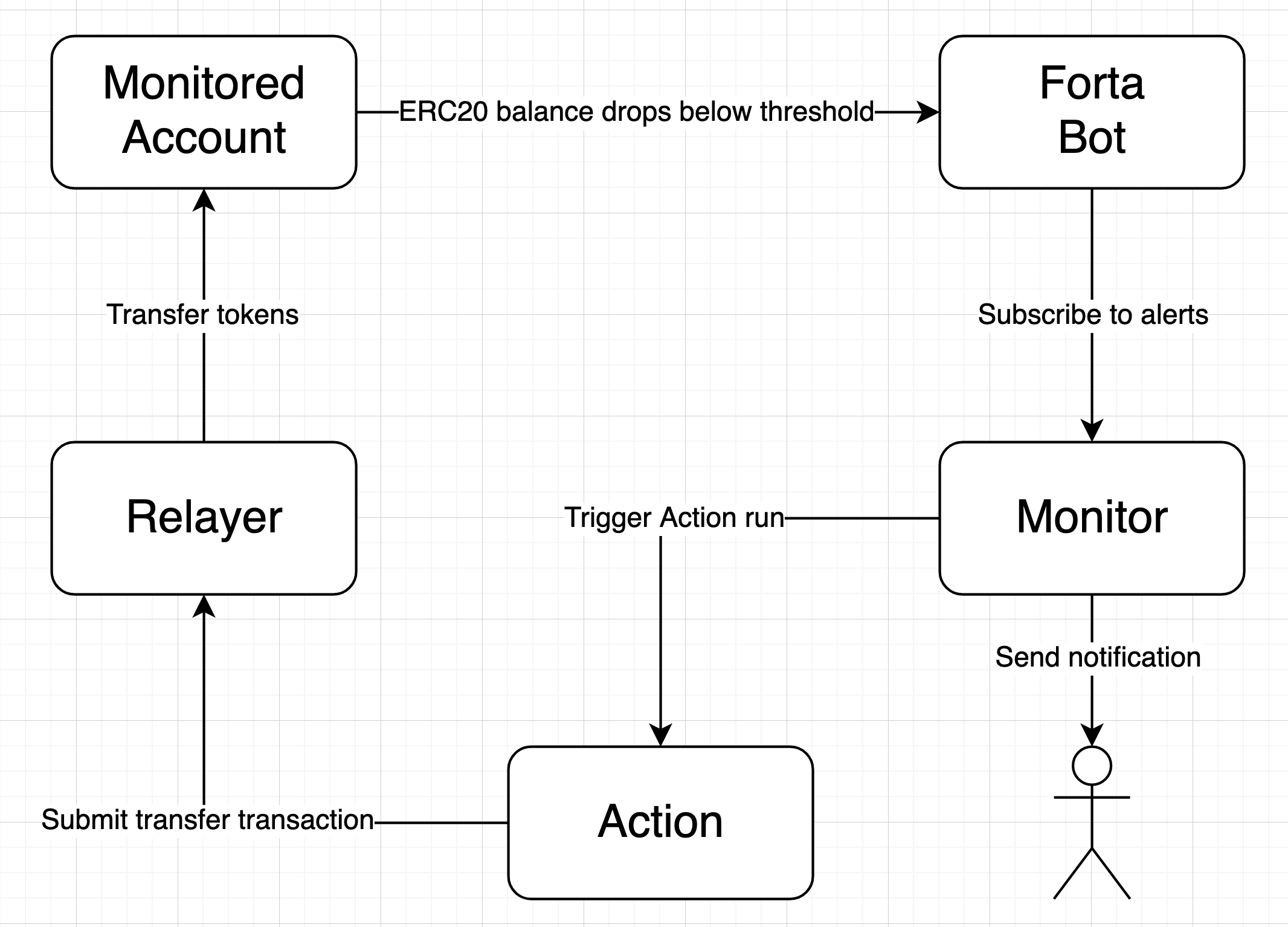
Defender allows you to integrate a custom Forta bot with Relayers, Actions, and Monitors. This guide will walk you through the steps of creating each of these components, as well as the Forta bot itself. The final goal is to have a setup that monitors the LINK balance of an account using a Forta Monitor, automatically topping up the account using Actions when the balance falls below a certain threshold. This guide uses LINK as the token to monitor on Polygon mainnet (LINK can be substituted with any ERC20 token, and works with any Defender, private, or forked network).
Pre-requisites
-
OpenZeppelin Defender account. You can sign up to Defender here.
1. Install Dependencies
Although this guide makes use of the defender-sdk package to create a Relayer, Monitor, and Action, the very same functionality is also available via the Defender web interface.
|
You’ll need to install the relevant Defender NPM packages. Note that Forta bot creation also requires that you also have Docker installed.
$ mkdir balance-automation && cd balance-automation
$ npm init -y
$ npm i --save-dev @openzeppelin/defender-sdk dotenv2. Create Relayer
From Defender, navigate to the API keys creation page in order to create a key set to use in the project. The capabilities of the key should include:
-
Manage Relayers
-
Manage Actions
-
Manage Monitors
Copy the key and secret, and create a .env file in the project root directory to paste it there.
API_KEY='key'
API_SECRET='secret'With the @openzeppelin/defender-sdk package, use the following script to create a new Relayer on Polygon and save the Relayer’s ID to your .env file.
require('dotenv').config();
const { Defender } = require('@openzeppelin/defender-sdk');
const { appendFileSync } = require('fs');
async function main() {
const creds = { apiKey: process.env.API_KEY, apiSecret: process.env.API_SECRET };
const client = new Defender(creds);
const createParams = {
name: 'Balance Automation Relayer',
network: 'matic',
minBalance: BigInt(1e17).toString()
};
const relayer = await client.relay.create(createParams);
appendFileSync('.env', relayer.relayerId)
console.log('Relayer created: ', relayer);
}
if (require.main === module) {
main().catch(console.error);
}Save the file and run the script. Having the Relayer’s ID gives you all that you need to run transactions via an Action.
3. Create Action
Next, you’ll need to create an Action that uses ethers.js to transfer LINK from the c[integrated Relayer] to the account you would like to be monitored by the Forta bot.
$ mkdir action && touch action/index.jsIn the index.js file, include logic to run the transfer function:
// ...
async function handler(event) {
const provider = new DefenderRelayProvider(event)
const signer = new DefenderRelaySigner(event, provider, { speed: 'fast' })
const contract = new ethers.Contract(LINK_CONTRACT, ABI, signer)
const amount = ethers.utils.parseUnits("1.0", 18);
const tx = await contract.connect(signer).transfer(MONITORED_ADDRESS, amount);
}The Action is able to connect to the Relayer by specifying its ID during creation. Credential passing is handled automatically and securely.
Again, with the @openzeppelin/defender-sdk package, use the following script to create the Action using the code from action/index.js:
require('dotenv').config();
const { Defender } = require('@openzeppelin/defender-sdk');
const { appendFileSync } = require('fs')
async function main() {
const creds = { apiKey: process.env.API_KEY, apiSecret: process.env.API_SECRET };
const client = new Defender(creds);
client.action.validatePath('./action');
const encodedZippedCode = await client.action.getEncodedZippedCodeFromFolder('./action');
const params = {
name: 'Low balance transfer',
encodedZippedCode,
trigger: {
type: 'webhook'
},
paused: false,
// Use the ID of the previosuly created Relayer
relayerId: process.env.RELAYER_ID,
};
const action = await client.action.create(params);
console.log('Created Action with ID: ', action.autotaskId)
appendFileSync('.env', `\nACTION_ID="${action.autotaskId}"`)
}
if (require.main === module) {
main().catch(console.error);
}Save the script and run it. You will be able to find the ID of the created action in the .env file or on the Defender Actions page.
4. Set up Forta
Install Forta CLI
For this guide, you’ll use the command line package to work with Forta bot development.
$ mkdir forta-bot && cd forta-bot
$ npx forta-agent@latest init --typescriptA keyfile will be generated in ~/.forta that you’ll encrypt with a password.
Create bot
First, the bignumber package needs to be installed:
$ npm install --save-dev bignumberIn the /src directory, open the agent.ts file, replacing the starter code.
Export a handler method that checks whether the account balance has fallen below 0.1 LINK:
import BigNumber from 'bignumber.js'
import {
BlockEvent,
Finding,
HandleBlock,
FindingSeverity,
FindingType,
getEthersProvider,
ethers
} from 'forta-agent'
export const ABI = `[ { "constant": true, "inputs": [ { "name": "_owner", "type": "address" } ], "name": "balanceOf", "outputs": [ { "name": "balance", "type": "uint256" } ], "payable": false, "type": "function" } ]`
export const ACCOUNT = "[Your Account Address]" // The account you'd like to monitor
export const MIN_BALANCE = "100000000000000000" // 0.1 LINK
export const LINK = "0xb0897686c545045afc77cf20ec7a532e3120e0f1" // LINK address on Polygon
const ethersProvider = getEthersProvider()
function provideHandleBlock(ethersProvider: ethers.providers.JsonRpcProvider): HandleBlock {
return async function handleBlock(blockEvent: BlockEvent) {
// report finding if specified account balance falls below threshold
const findings: Finding[] = []
const erc20Contract = new ethers.Contract(LINK, ABI, ethersProvider)
const accountBalance = new BigNumber((await erc20Contract.balanceOf(ACCOUNT, {blockTag:blockEvent.blockNumber})).toString())
if (accountBalance.isGreaterThanOrEqualTo(MIN_BALANCE)) return findings
findings.push(
Finding.fromObject({
name: "Minimum Account Balance",
description: `Account balance (${accountBalance.toString()}) below threshold (${MIN_BALANCE})`,
alertId: "FORTA-6",
severity: FindingSeverity.Info,
type: FindingType.Suspicious,
metadata: {
balance: accountBalance.toString()
}
}
))
return findings
}
}
export default {
provideHandleBlock,
handleBlock: provideHandleBlock(ethersProvider)
}Edit package.json, giving your bot a unique name (in lowercase) and description, specifying the chainId.
{
"name": "minimum-link-balance-polygon-example",
"version": "0.0.1",
"description": "Forta bot that reports whether an account has fallen below 0.1 LINK balance",
"chainIds": [137],
...
}You can test the bot’s functionality using live blockchain data by running it locally, ensuring that you specify an account in the code with no LINK.
$ npx hardhat forta:runDeploy bot
Now, you will deploy the bot via the CLI. Keep in mind that the account you’re deploying from needs to be funded with MATIC.
$ npm run publishThis will build the agent image and push it to the remote repository.
After entering the password you used when installing forta-agent`, you’ll be given the agent ID and manifest.
❯ npm run publish
> minimum-link-balance-polygon-example@0.0.1 publish
> forta-agent publish
building agent image...
pushing agent image to repository...
✔ Enter password to decrypt keyfile UTC--2024-01-03T21:52:34.343Z--3c89fa18f6cb70585b5831970e6b0c067ae46598 … ********
pushing agent documentation to IPFS...
pushing agent manifest to IPFS...
adding agent to registry...
successfully added agent id 0xd6d29c1584801d5baa867c9edaf595e794be63d207758155f28bed8ffa98d472 with manifest QmSNSaNwbjcvi2SuX73pqzEUcTzb4zdXpjPRbiCzsBLKuoCongratulations on deploying a Forta bot!
For convenience, save the agent ID to the .env file in your main project folder. You’ll need it when creating a Monitor that subscribes to this bot.
5. Create Forta Monitor
With the @openzeppelin/defender-sdk package, use the following script to create a Forta Monitor connected to your Relayer and Action.
require('dotenv').config();
const { Defender } = require('@openzeppelin/defender-sdk');
const BOT = process.env.BOT_ID
async function main() {
const creds = { apiKey: process.env.API_KEY, apiSecret: process.env.API_SECRET };
const client = new Defender(creds);
const notificationChannels = await client.listNotificationChannels();
const { notificationId, type } = notificationChannels[0];
const requestParams = {
type: 'FORTA',
name: 'Low balance alert - trigger refill',
agentIDs: [BOT],
fortaConditions: {
minimumScannerCount: 2,
severity: 1, // (unknown=0, info=1, low=2, medium=3, high=4, critical=5)
},
autotaskTrigger: process.env.ACTION_ID,
alertTimeoutMs: 120000,
notificationChannels: [notificationChannels[0].notificationId],
};
const monitor = await client.monitor.create(requestParams);
console.log(monitor)
}
if (require.main === module) {
main().catch(console.error);
}The Monitor is configured to trigger a notification as well as an Action when the bot sends an alert. To prevent being triggered multiple times for the same low balance event, the alertTimeoutMs has been set. Run the script to create the Monitor.
Congratulations! You can now experiment with this integration further by transfering LINK from the monitored account so that the LINK balance drops below 0.1. When the Forta bot detects this, it will trigger the Monitor, which sends a notification and runs the Action to refill the monitored account.